Anatomy
Kidneys are located in the abdominal cavity. There are two, one on each side of the spine. The asymmetry within the abdominal cavity caused by the liver typically results in the right kidney being slightly lower than the left, and left kidney being located slightly more medial than the right.
The kidney has a bean-shaped structure; each kidney has a convex and concave surface. The concave surface, the renal hilum, is the point at which the renal artery enters the organ, and the renal vein and ureter leave.
The kidney is approximately 11–14 cm in length, 6 cm wide and 4 cm thick. It contains about a million nephrons, which are like tiny pouches. Each nephron has a filter at one end, called a glomerulus, to filter the blood. When this filtration process is not possible by the kidney, one needs a dialysis to done by a special machine to filter harmful wastes, salt, and excess fluid from your blood. The function of the kidney can be measured by how quickly blood is filtered through these glomeruli.
Functions
Kidneys are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and regulation of blood pressure (via maintaining salt and water balance). They serve the body as a natural filter of the blood, and remove wastes which are diverted to the urinary bladder. In producing urine,bouncy castle for sale the kidneys excrete wastes such as urea and ammonium, and they are also responsible for the reabsorption of water, glucose, and amino acids. The kidneys also produce hormones including calcitriol, erythropoietin, and the enzyme renin.
Causes of Kidneys Disorder
Any of the following conditions may lead to kidneys disorder:
• High blood pressure
• High Cholesterol
• Heart disease
• Diabetes mellitus type 1 or type 2
• Liver disease
• Sickle cell disease
• Arteritis
• Fibromuscular dysplasia of arteries
• Vesicoureteral reflux (an abnormal movement of urine, which travels from the bladder the wrong way back toward the kidney)
Symptoms of Kidneys Disorder
If the kidneys malfunction, urea builds up in the body, accumulating in the kidneys, bloodstream and elsewhere. This condition called azotaemia, which refers to the insufficient filtering of blood by the kidneys.
Azotaemia can be mild with no symptoms but, if the waste continues to build up, the kidney functions gradually fails to function. When almost 80% of kidney function is lost, it is called uraemia, which describes the illness accompanying kidney (or renal) failure.
Kidney malfunctions may not be immediately noticeable because the remaining healthy kidney cells compensate for the damaged ones. Generally, kidneys disorder can only be detected in urine tests. It is therefore important to monitor the situation if any of the following symptoms exists:
• Water retention and generalized swelling, especially noticeable in the limbs
• High blood pressure.
• Heart failure
• Nausea
• Vomiting
• Weight loss
• Severe headaches
• Itchiness of the skin
• Fluid around the lungs
• Ulcers in the mouth
• Extreme fatigue
• Blood in the stool
• Impaired mental function
Yoga Therapy
Practice of asana, pranayama and kriyas (cleansing techniques) can keep the internal organs healthy, particularly improving the overall function of the kidneys.
Asanas like gentle twist and backbends contracts and massages the kidneys. The practice enables and activates the efficient function of the kidneys.
Practice of pranayama like Nadi Sodhana, Anuloma- Viloma can control and balance the nervous system and relieve the mind from stress.
Kriyas are great cleansing techniques to remove the toxins out of the body. By purifying the entire system, one feels light and blood is cleansed by the flow of the prana to every single cell of the body.
Here are some asanas which combine both backbends and twist together for healthy kidneys.
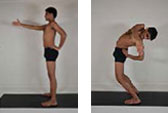 Kati Chakrasana (Waist Twisted Pose)
Kati Chakrasana (Waist Twisted Pose)
1. Stand in Tadasana with the legs hip width apart.
2. Stretch the right arm forward, while resting the left palm on the waist.
3. Push the hip slightly forward and twist the body to the left, keeping the feet firm and knees slightly bent.
4. Stay for about 10-20 seconds and repeat the same on the other side. Repeat the whole process about 2-3 times.
Benefit: This decreases the rigidity of the spine and massages the kidneys.
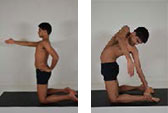 Ustrasana (Camel Pose)
Ustrasana (Camel Pose)
1. Kneel on the mat with knees slightly apart, pressing the toes flat on the mat. Stretch the right arm forward, while resting the left palm on the hips.
2. Push the hip forward, pull the thighs up and lift the spine, expanding the ribs.
3. Exhale, reach the left hand back and catch on the left heel firmly.
4. Twist the whole trunk to the left side, gazing at the left foot with the right hand pointing down.
5. Stay in this pose with even breath, feeling the twist
6. Stay for about 10-20 seconds. Repeat the same on the other side.
Benefit: This pose stimulates the kidneys, pancreas brincolin and thyroids glands. It improves the lung capacity and circulation.
 Tiryaka Bhujangasana (Twisted Cobra Pose)
Tiryaka Bhujangasana (Twisted Cobra Pose)
1. Lie on the stomach.
2. Stretch the legs with pointed toes.
3. Keep the palms on the sides of the chest. Press the palms on the mat and raise the abdomen and chest upwards.
4. Exhale, turn the head and shoulders to the left side, gazing at the left foot.
5. Stay for 20-30 seconds and repeat the same on the right side. Repeat the whole process for 2-3 rounds.
Benefit: This pose squeezes kidneys from the side and the abdomen stimulating the intestine.
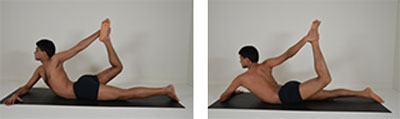
Eka Hasta Dhanurasana (One Hand Bow Pose)
1. Lie on the stomach.
2. Stretch the legs with pointed toes.
3. Bend the right elbow with the forearm slightly forward.
4. Bend the right knee, catching the right foot with the left hand from the outer edge.
5. Inhale, raise the chest up.
6. Exhale, pull the foot and lift the thigh upwards.
7. Stay for 20-30seconds and repeat on the other side.
Benefit: This stimulates the kidneys by improving digestion and elimination.
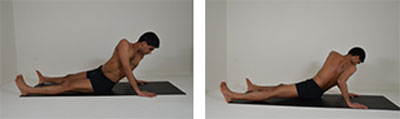
Bhunamanasana (Earth Worship Pose)
1. Sit with the spine erect and legs stretched out with the feet apart.
2. Exhale, revolve the trunk towards the back, placing the palms on the mat shoulder width apart.
3. Inhale, lengthen the spine.
4. Exhale, bend the elbows and either fold forward towards the mat to the extent possible or stay half way and go down gradually.
5. Stay for 5-10 second and repeat the same on the other side. Repeat the whole process for about 5 rounds each side.
Benefits: This keeps the spine supple and kidneys active.
Conclusion
Amongst other benefits, yoga controls the stress level, which is key to improving overall health. Regular and active practice of asanas and pranayama can help control the blood pressure and reduce the risk of chronic kidney diseases. A focused practice could either alleviate the effects of the kidney diseases.
Practice aside, a healthy diet is critical for preventing chronic kidney disease. Proper diet helps lower the amount of cholesterol and regulate blood pressure.
Avoid taking too much of painkiller or any drug without the advice of the doctor because this can damage the kidneys. Further, consult the doctor timely and regularly, especially in situations of diabetes or high blood pressure.
Prevention is better than cure. Hence, proper and early diagnosis with quick intervention is important for all potential illnesses, including severe kidneys disease.















 Other
Other